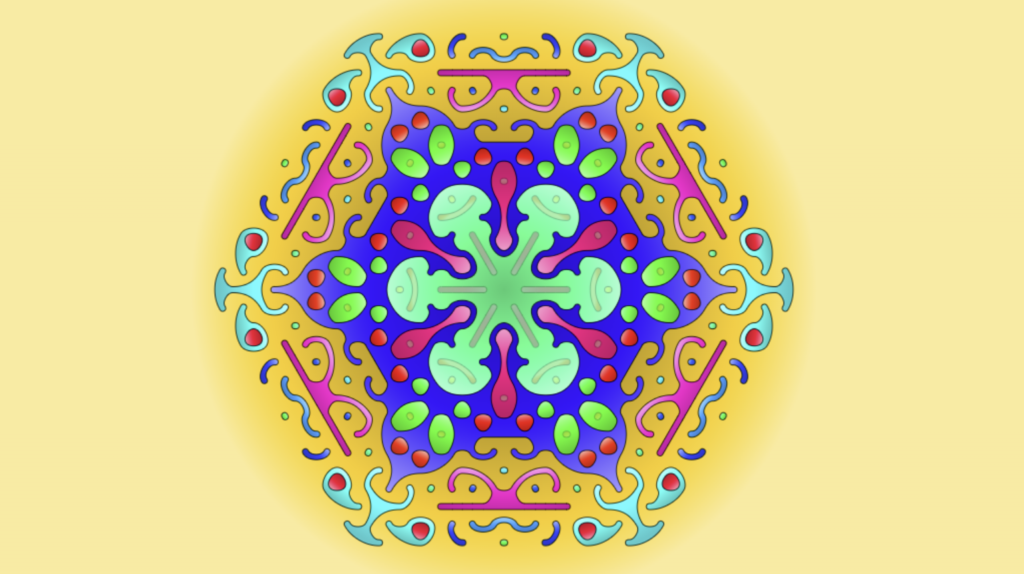
Hey there! Ever wanted to bring some interactive fun to your web projects? Check out this dynamic canvas example where you can create and animate different shapes just by clicking a button. Whether you’re into circles, squares, or triangles, this code lets you easily switch between them, each with its own vibrant color and design. It’s a great way to see how canvas manipulation works and how you can animate shapes to create a lively, engaging experience. Dive in, play around, and let your creativity shine!
<div id="menu" class="hidden">
<p id="controls">controls</p>
<div id="showhide">
<hr>
<p><input type="range" min=0.02 max=0.06 step="any" value=0.04 id="cellsize"> cell size</p>
<p>geometry choice: <select id="geometrychoice">
<option value="1">2</option>
<option value="2">1 - 2</option>
<option value="3">2 - 3</option>
<option value="4" selected>1 - 2 - 3</option>
</select></p>
<p>color mode: <select id="colormode">
<option value="1">colorful</option>
<option value="2" selected>colorful - brighter</option>
<option value="3">bicolor</option>
<option value="4">monochrome</option>
<option value="5">grey</option>
</select></p>
<p>with stroke <input type="checkbox" id="stroke" checked></p>
<p>random <input type="checkbox" id="random" checked></p>
</div> <!-- showhide -->
</div> <!-- menu --><style>
body {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, "Liberation Sans", FreeSans, sans-serif;
background-color: #000;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border-width: 0;
}
input {
caret-color: auto;
}
#menu {
font-size: 80%;
margin: 0;
padding: 5px;
position: absolute;
left: 5px;
top: 5px;
border-radius: 10px;
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 128, 0.9);
color: black;
z-index: 10;
}
#menu.hidden #showhide {
display: none;
}
#controls {
margin-top: 0px;
margin-bottom: 0px;
}
#menu button {
margin-right: 5px;
margin-left: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
#menu .center {
text-align: center;
}
</style><script>
"use strict";
/* at the last step of the design, I rotated the drawing by 90 degrees for a better result.
I did not update my variable names and comments accordingly. Keep this in mind when trying to understand my code :
1st coordinates (x) of points actually refer to the vertical direction
2nd coordinates (y) refer to the horizontal direction
*/
/* table relProbaNbPoints gives the RELATIVE probability used to attribute 0 to 3 points
to each side of an hexagon.
It should contain integer values in the range 0..20.
*/
const tbRelProbaNbPoints = [
[0, 0, 1, 0], // allways 2
[0, 1, 1, 0], // 1-2
[0, 0, 2, 1], // 2-3
[0, 1, 1, 1]
]; // never 0
let geometryChoice = 3; // 1-2-3
let rayHex = 70; // circumradius of hexagon - general scale of drawing
let nbLayers;
const neighborDx = [1, 0, -1, -1, 0, 1];
const neighborDy = [0, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1];
let messages;
let canv, ctx; // canvas and context : global variables (I know :( )
let ctxAnim;
let maxx, maxy; // canvas sizes (in pixels)
let grid; // array of hexagons
let tbLoops; // loops array
let hierar; // hierarchical structure for loops
let algoPick; // two algorithms are available to pick points, this variable tells which is chosen
let lRef;
let ui, uiv;
let perpendicular = []; // for easy calculation of perpendiculars to hexagon edges
let vertices; // positions of vertices of one Hexagon, relative to center
let tbNbPoints; // table for choice of nb of points on each side
// shortcuts for Math.…
const mrandom = Math.random;
const mfloor = Math.floor;
const mround = Math.round;
const mceil = Math.ceil;
const mabs = Math.abs;
const mmin = Math.min;
const mmax = Math.max;
const mPI = Math.PI;
const mPIS2 = Math.PI / 2;
const m2PI = Math.PI * 2;
const msin = Math.sin;
const mcos = Math.cos;
const matan2 = Math.atan2;
const mhypot = Math.hypot;
const msqrt = Math.sqrt;
const rac3 = msqrt(3);
const rac3s2 = rac3 / 2;
const mPIS3 = Math.PI / 3;
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// miscellaneous functions
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function alea(min, max) {
// random number [min..max[ . If no max is provided, [0..min[
if (typeof max == "undefined") return min * mrandom();
return min + (max - min) * mrandom();
}
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function intAlea(min, max) {
// random integer number [min..max[ . If no max is provided, [0..min[
if (typeof max == "undefined") {
max = min;
min = 0;
}
return mfloor(min + (max - min) * mrandom());
} // intAlea
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
/* returns intermediate point between p0 and p1,
alpha = 0 will return p0, alpha = 1 will return p1
values of alpha outside [0,1] may be used to compute points outside the p0-p1 segment
*/
function lerp(p0, p1, alpha) {
return [
(1 - alpha) * p0[0] + alpha * p1[0],
(1 - alpha) * p0[1] + alpha * p1[1]
];
} // function lerp
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function arrayShuffle(array) {
/* randomly changes the order of items in an array
only the order is modified, not the elements
*/
let k1, temp;
for (let k = array.length - 1; k >= 1; --k) {
k1 = intAlea(0, k + 1);
temp = array[k];
array[k] = array[k1];
array[k1] = temp;
} // for k
return array;
} // arrayShuffle
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function prod(mat4, mat) {
// mat may be mat2 or mat4
// returns mat of same type as mat
/* mat4 : 0 1
2 3
*/
if (mat.length == 2)
return [
mat4[0] * mat[0] + mat4[1] * mat[1],
mat4[2] * mat[0] + mat4[3] * mat[1]
];
else
return [
mat4[0] * mat[0] + mat4[1] * mat[2],
mat4[0] * mat[1] + mat4[1] * mat[3],
mat4[2] * mat[0] + mat4[3] * mat[2],
mat4[2] * mat[1] + mat4[3] * mat[3]
];
}
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function distance(p0, p1) {
/* distance between points */
return mhypot(p0[0] - p1[0], p0[1] - p1[1]);
} // function distance
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// User Interface (controls)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function toggleMenu() {
if (menu.classList.contains("hidden")) {
menu.classList.remove("hidden");
this.innerHTML = "close controls";
} else {
menu.classList.add("hidden");
this.innerHTML = "controls";
}
} // toggleMenu
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function getCoerce(name, min, max, isInt) {
let parse = isInt ? parseInt : parseFloat;
let ctrl = ui[name];
let x = parse(ctrl.value, 10);
if (isNaN(x)) {
x = uiv[name];
}
x = mmax(x, min);
x = mmin(x, max);
ctrl.value = uiv[name] = x;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function prepareUI() {
// toggle menu handler
document.querySelector("#controls").addEventListener("click", toggleMenu);
// toggleMenu.call(document.querySelector("#controls"));
ui = {}; // User Interface HTML elements
uiv = {}; // User Interface values of controls
["cellsize", "geometrychoice", "colormode", "stroke", "random"].forEach(
(ctrlName) => (ui[ctrlName] = document.getElementById(ctrlName))
);
registerControl("cellsize", readCoerced, "change");
registerControl("geometrychoice", readUIInt, "input");
registerControl("colormode", readUIInt, "input");
registerControl("stroke", readUICheck, "input");
registerControl("random", readUICheck, "input", setRandom);
readUI();
} // prepareUI
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function readUI() {
if (ui.registered) {
for (const ctrl in ui.registered) ui.registered[ctrl].readF();
}
setRandom.call(ui.random);
} // readUI
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function registerControl(
controlName,
readFunction,
changeEvent,
changedFunction
) {
/* provides simple way to associate controls with their read / update / changeEvent / changed functions
since many (but not all) controls work almost the same way */
/* changeEvent and changedFunction are optional */
const ctrl = ui[controlName];
ui.registered = ui.registered || [];
ui.registered.push(ctrl); // NEVER register a control twice !!!
ctrl.readF = readFunction;
if (changeEvent) {
ctrl.addEventListener(changeEvent, (event) => {
readFunction.call(ctrl);
if (changedFunction) changedFunction.call(ctrl, event);
});
}
} // registerControl
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function readUIFloat() {
uiv[this.id] = parseFloat(this.value);
}
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function readUIInt(ctrl, event) {
uiv[this.id] = parseInt(this.value);
}
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function readUICheck(ctrl, event) {
uiv[this.id] = this.checked;
}
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function readCoerced() {
/* the element will be read with getCoerce with values given by its min, max and step attributes
(integer value if step == 1)
*/
let min = this.getAttribute("min");
let max = this.getAttribute("max");
let step = this.getAttribute("step");
getCoerce(this.id, min, max, step == 1);
}
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function setRandom() {
["cellsize", "geometrychoice", "colormode", "stroke"].forEach(
(elem) => (ui[elem].disabled = this.checked)
);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
class ExtremeRadialFilter {
/* tracks extreme radiito build a radial gradient
*/
constructor() {
this.rmin = Infinity;
this.rmax = -Infinity;
}
filter(p) {
let rad = mhypot(p[0], p[1]);
this.rmin = mmin(this.rmin, rad);
this.rmax = mmax(this.rmax, rad);
} // filter
filterBezier(p0, p1, p2, p3) {
/* recursively divides bezier curve into pieces, until each piece is almost a straight ligne, and filters individual points
the "almost a straight line" is arbitrarily defined
*/
this.filter(p0);
this.filter(p3);
(function interm(p0, p1, p2, p3) {
if (
distance(p0, p1) + distance(p1, p2) + distance(p2, p3) <
1.1 * distance(p0, p3)
)
return; // almost straight
const pa = lerp(p0, p1, 0.5);
const pb = lerp(p1, p2, 0.5);
const pc = lerp(p2, p3, 0.5);
const pd = lerp(pa, pb, 0.5);
const pe = lerp(pb, pc, 0.5);
const pf = lerp(pd, pe, 0.5);
this.filter(pf); // filter intermediate point
interm.call(this, p0, pa, pd, pf); // check subparts of Bézier curve
interm.call(this, pf, pe, pc, p3);
}.call(this, p0, p1, p2, p3));
}
getRadialGradient() {
/* creates a gradient without filling the stop points */
/* not suitable for"ring" loops */
return ctx.createRadialGradient(0, 0, this.rmin, 0, 0, this.rmax);
}
} // ExtremeRadialFilter
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function getKey(kx, ky) {
/* key used to identify hexagons in grids
*/
return `${kx},${ky}`;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
class Hexagon {
constructor(kx, ky) {
/* vertices are numbered 0 to 5 in order : E, SE, SW, W, NW, NE
edges are numbered 0 to 5, edge k is betwxeen vertices k and (k + 1) % 6
hexagon (kx=0, ky=0) is at center of display
kx increases crossing edge 0 and decreases crossing edge 3
ky increases crossing edge 1 and decreases crossing edge 3
symmetry axes meet at the center of tile 0,0
axis A is horizontal
axis B is at 30° turning clockwise from axis 0
All the "axis" stuff below is only meaningful for Hexagons in 1st sector ( kx-2y >= 0 && ky <=0)
*/
this.kx = kx;
this.ky = ky;
this.isOnAxisA = kx == -2 * ky;
this.isAlongAxisA = kx - 1 == -2 * ky; // has its side 4 on axis A
this.isOnAxisB = ky == 0;
this.noAxis = !(this.isOnAxisA || this.isOnAxisB);
} // constructor
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
size() {
/* computes screen sizes / positions
*/
// centre
this.xc = this.kx * 1.5 * rayHex;
this.yc = (this.ky + this.kx / 2) * rayHex * rac3;
this.vertices = [[], [], [], [], [], []];
// x coordinates of this hexagon vertices
this.vertices[3][0] = this.xc + vertices[3][0];
this.vertices[2][0] = this.vertices[4][0] = this.xc + vertices[2][0];
this.vertices[1][0] = this.vertices[5][0] = this.xc + vertices[1][0];
this.vertices[0][0] = this.xc + vertices[0][0];
// y coordinates of this hexagon vertices
this.vertices[4][1] = this.vertices[5][1] = this.yc + vertices[4][1];
this.vertices[0][1] = this.vertices[3][1] = this.yc + vertices[0][1];
this.vertices[1][1] = this.vertices[2][1] = this.yc + vertices[1][1];
if (!this.nbPPSide) return;
/* positions of intermediate points on sides */
/* depends on the number of points on this side */
this.points = [];
this.nbPPSide.forEach((nbPoints, kcote) => {
let p0 = this.vertices[kcote];
let p1 = this.vertices[(kcote + 1) % 6];
switch (nbPoints) {
case 0:
break; // no point at all, nothing to compute
case 1:
this.points.push(lerp(p0, p1, 1 / 2));
break;
case 2:
this.points.push(lerp(p0, p1, 3 / 8)); // better results than 1/3 and 2/3
this.points.push(lerp(p0, p1, 5 / 8));
break;
case 3:
this.points.push(lerp(p0, p1, 9 / 32)); // better results than 1/4, 2/4 and 3/4
this.points.push(lerp(p0, p1, 1 / 2));
this.points.push(lerp(p0, p1, 23 / 32));
break;
} // switch
}); // hexa.nbPPSide.forEach
} // Hexagon.prototype.size
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
structurePoints() {
/* after nbPPSide has been initialised, prepares a few structures to make points manupulation easier */
this.sideOfPoint = [];
for (let kCote = 0; kCote < 6; ++kCote) {
for (let k = 0; k < this.nbPPSide[kCote]; ++k)
this.sideOfPoint.push(kCote);
} // for kcote
/* compute, for each side of the current Hexagon, which points belong to it */
this.pointsOfSide = [[], [], [], [], [], []];
for (let k = 0; k < this.nbPoints; ++k)
this.pointsOfSide[this.sideOfPoint[k]].push(k);
/* create the set of points that can be connected together in one hexagon
- initially all of them */
this.connectables = [[]];
for (let kin = 0; kin < this.nbPoints; ++kin)
this.connectables[0][kin] = kin;
}
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
isAllowableForStart(kp) {
/* only meaningful for hexagons in sector 0 */
const sop = this.sideOfPoint[kp];
if (this.kx == 0 && this.ky == 0) return kp == 0;
if (this.isOnAxisA) return sop < 3;
if (this.isOnAxisB)
return (
[4, 5].includes(sop) ||
(sop == 3 && this.pointsOfSide[3][1] == kp) ||
(sop == 0 && 0 == kp)
);
return true;
} // isAllowableForStart
// - - - - -x- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
areCompatibleForSymmetry(kp0, kp1) {
// returns false if this Hexagon has one or more symmetry axis, and points are not compatible with at least one of the symmetries
// returns false if not compatible, "A","B" if symmetrical about one of the axis, and true if compatible without symmetry
if (this.noAxis) return true; // easy
let side0 = this.sideOfPoint[kp0],
side1 = this.sideOfPoint[kp1];
let pos0 = this.pointsOfSide[side0].indexOf(kp0),
pos1 = this.pointsOfSide[side1].indexOf(kp1);
let symm;
if (this.isOnAxisA) {
if ([0, 1, 2].includes(side0) != [0, 1, 2].includes(side1)) {
// if on different sides of axis
if (side0 + side1 != 5) return false; // not symmetrical sides !
if (pos0 + pos1 + 1 != this.nbPPSide[side0]) return false;
symm = "A";
}
}
if (this.isOnAxisB) {
if (
([1, 2].includes(side0) ||
(side0 == 0 && pos0 == 1) ||
(side0 == 3 && pos0 == 0)) !=
([1, 2].includes(side1) ||
(side1 == 0 && pos1 == 1) ||
(side1 == 3 && pos1 == 0))
) {
// if on different sides of axis
if ((side0 + side1) % 6 != 0) return false;
if (pos0 + pos1 + 1 != this.nbPPSide[side0]) return false;
symm = "B";
}
}
if (this.kx == 0 && this.ky == 0) {
if ((kp0 + 1) % 12 != kp1 && (kp0 + 11) % 12 != kp1) return false;
}
return symm || true;
}
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
pickFromConnectables(kin) {
let kconn, idxconn0, idxconn, acceptable, kout;
// look for set of connectables containing kin
for (kconn = 0; kconn < this.connectables.length; ++kconn) {
if ((idxconn0 = this.connectables[kconn].indexOf(kin)) != -1) break; // found it
} // for
let ktry = 1;
do {
switch (algoPick) {
case 0:
idxconn =
intAlea(this.connectables[kconn].length / 2) * 2 +
((idxconn0 & 1) ^ 1);
break;
case 1:
idxconn = (idxconn0 + ktry) % this.connectables[kconn].length;
}
kout = this.connectables[kconn][idxconn];
acceptable = this.areCompatibleForSymmetry(kin, kout);
ktry += 2;
} while (!acceptable);
return { kout, symm: acceptable === true ? false : acceptable };
} // pickFromConnectables
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
connect(kin, kout) {
/* manages the 'connectables' property wich tells which points may be connected together
without cutting a previously created connection
/* normally, kin et kout should have different parities */
let kcon = 0; // index of subset of 'connectables' which contains kin et kout
let k0, k1;
while (true) {
k0 = this.connectables[kcon].indexOf(kin);
if (k0 >= 0) {
k1 = this.connectables[kcon].indexOf(kout);
if (k1 < k0) [k0, k1] = [k1, k0];
// put apart points associated with kin and kout
let narr = this.connectables[kcon].splice(k0, k1 + 1 - k0);
// remove kin and kout from 'connectables' since they now are used
narr.shift();
narr.pop();
if (narr.length > 0) this.connectables.push(narr); // the rest becomes a new 'connectable' subset
if (this.connectables[kcon].length == 0)
this.connectables.splice(kcon, 1); // remove subset if empty
return; // that's all folks
} // if kin was found
// not found here, go further
++kcon;
} // while...
} // Hexagon.prototype.connect
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
// returns a pair of values {kx, ky}
neighbour(side) {
return grid.get(
getKey(this.kx + neighborDx[side], this.ky + neighborDy[side])
);
} // Hexagon.prototype.neighbour
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
otherPoint(kp) {
/* returns hexagon and index of point which is physically the same as given point */
let side = this.sideOfPoint[kp];
let nbOnSide = this.pointsOfSide[side].length;
let posOnSide = this.pointsOfSide[side].indexOf(kp);
const otherHex = this.neighbour(side);
const otherSide = (side + 3) % 6;
return {
hexa: otherHex,
kp: otherHex.pointsOfSide[otherSide][nbOnSide - 1 - posOnSide]
};
} // otherPoint
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
} // end of class Hexagon
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function createGrid() {
// creates the "sector 0" of the grid of Hexagons
let hexa, side, sum, nbPPs, neighbor, nbp, n1;
/* create table for choice of nbPoints */
tbNbPoints = [];
tbRelProbaNbPoints[geometryChoice].forEach((frq, nb) => {
for (let k = 0; k < frq; ++k) tbNbPoints.push(nb);
}); // relProbaNbPoints.forEach
function rndNb() {
return tbNbPoints[intAlea(tbNbPoints.length)];
}
grid = new Map();
/* special central tile */
hexa = new Hexagon(0, 0);
grid.set("0,0", hexa);
hexa.nbPPSide = [];
grid.set(getKey(0, 0), hexa);
let frontier = [hexa];
nbLayers = mmin(
mfloor((maxy / 2 / rayHex - 1) / 1.5),
mfloor(maxx / 2 / rayHex / rac3 - 0.3)
);
for (let d = 1; d <= nbLayers; ++d) {
const newFrontier = [];
let hexa = frontier[0];
if (!hexa.isOnAxisA)
newFrontier.push(
new Hexagon(hexa.kx + neighborDx[5], hexa.ky + neighborDy[5])
);
frontier.forEach((hexa) =>
newFrontier.push(
new Hexagon(hexa.kx + neighborDx[0], hexa.ky + neighborDy[0])
)
);
// add new Frontier to grid and add points on edges
newFrontier.forEach((hexa) => {
grid.set(getKey(hexa.kx, hexa.ky), hexa);
do {
hexa.nbPPSide = [];
// apply neighborhood constraint first
for (let k = 0; k < 6; ++k) {
let neighHex = hexa.neighbour(k);
if (
neighHex &&
neighHex.nbPPSide &&
neighHex.nbPPSide[(k + 3) % 6] !== undefined
) {
// constrained by neighbor
hexa.nbPPSide[k] = neighHex.nbPPSide[(k + 3) % 6];
} else if (d == nbLayers) {
// constrained to be 0 on exterior
if (k == 0) hexa.nbPPSide[k] = 0;
if (k == 5 && hexa.ky <= 0) hexa.nbPPSide[k] = 0;
if (k == 1 && hexa.ky >= 0) hexa.nbPPSide[k] = 0;
}
} // for k
// apply symmetry constraints now
for (let k = 0; k < 6; ++k) {
if (hexa.nbPPSide[k] !== undefined) continue;
if (
hexa.isOnAxisA &&
hexa.nbPPSide[[5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0][k]] !== undefined
) {
// constrained by symmetry around axis A
hexa.nbPPSide[k] = hexa.nbPPSide[[5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0][k]];
}
if (hexa.isOnAxisB) {
if (k == 0 || k == 3) hexa.nbPPSide[k] = 2;
else if (hexa.nbPPSide[[0, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1][k]] !== undefined) {
// constrained by symmetry around axis B
hexa.nbPPSide[k] = hexa.nbPPSide[[0, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1][k]];
}
}
if (hexa.nbPPSide[k] === undefined) hexa.nbPPSide[k] = rndNb();
}
hexa.nbPoints = hexa.nbPPSide.reduce((s, v) => s + v);
} while (hexa.nbPoints & 1); // want an even sum !
}); // newFrontier.forEach
frontier = newFrontier;
} // for d
// for hex (0,0), same number on 6 sides
grid.get("0,0").nbPPSide = new Array(6).fill(2);
grid.get("0,0").nbPoints = 6 * grid.get("0,0").nbPPSide[0];
grid.forEach((hexa) => hexa.structurePoints());
} // createGrid
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function symmAP(p) {
return [p[0], -p[1]];
}
function symmBP(p) {
return prod([0.5, rac3s2, rac3s2, -0.5], p);
}
const matrot60 = [0.5, -rac3s2, rac3s2, 0.5];
function rot60P(p) {
return prod(matrot60, p);
}
const matrot120 = prod(matrot60, matrot60);
function rot120P(p) {
return prod(matrot120, p);
}
function rot180P(p) {
return prod([-1, 0, 0, -1], p);
}
const matrot240 = prod(matrot120, matrot120);
function rot240P(p) {
return prod(matrot240, p);
}
const matrot300 = prod(matrot240, matrot60);
function rot300P(p) {
return prod(matrot300, p);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function takeSymA(bezier) {
return [
symmAP(bezier[3]),
symmAP(bezier[2]),
symmAP(bezier[1]),
symmAP(bezier[0])
];
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function takeSymB(bezier) {
return [
symmBP(bezier[3]),
symmBP(bezier[2]),
symmBP(bezier[1]),
symmBP(bezier[0])
];
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function takeRot60B(bezier) {
return bezier.map(rot60P);
}
function takeRot120B(bezier) {
return bezier.map(rot120P);
}
function takeRot180B(bezier) {
return bezier.map(rot180P);
}
function takeRot240B(bezier) {
return bezier.map(rot240P);
}
function takeRot300B(bezier) {
return bezier.map(rot300P);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function makeLoops() {
tbLoops = [];
algoPick = intAlea(2); // choice of algorithme
const ngrid = arrayShuffle(Array.from(grid));
ngrid.forEach((elem) => {
const hexa = elem[1];
const startkp = arrayShuffle(
new Array(hexa.nbPoints).fill(0).map((v, k) => k)
);
for (let k = 0; k < startkp.length; ++k) {
const list = [];
hexa.connectables.forEach((c) => c.forEach((kk) => list.push(kk)));
if (list.length == 0) break;
let kp = startkp[k];
if (!list.includes(kp)) continue;
if (!hexa.isAllowableForStart(kp)) continue;
let loop = makeOneLoop(hexa, kp);
tbLoops.push(loop);
} // for k
return;
});
function makeOneLoop(hexa, kp) {
const loop = prepareOneLoop(hexa, kp);
// add every crossing actual points (in pixels) of BezierCurve
loop.crossings.forEach((cr) => {
cr.bezier = toBezier({
hexagon: cr.hexa,
ksidein: cr.hexa.sideOfPoint[cr.kin],
ksideout: cr.hexa.sideOfPoint[cr.kout],
pin: cr.hexa.points[cr.kin],
pout: cr.hexa.points[cr.kout]
});
});
if (loop.symA || loop.endA) {
let ncr = loop.crossings.length;
for (let k = ncr - 1; k >= 0; --k) {
if (loop.crossings[k].symm !== "A")
loop.crossings.push({ bezier: takeSymA(loop.crossings[k].bezier) }); // only the bezier field is useful here
}
}
if (loop.symB || loop.endB) {
let ncr = loop.crossings.length;
for (let k = ncr - 1; k >= 0; --k) {
if (loop.crossings[k].symm !== "B")
loop.crossings.push({ bezier: takeSymB(loop.crossings[k].bezier) }); // only the bezier field is useful here
}
}
if (loop.ring) {
if (loop.crossings[0].symm && loop.crossings.length > 1)
loop.crossings.pop(); // remove crossing doubled by symmetry
let ncr = loop.crossings.length;
if (loop.endB) {
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({ bezier: takeRot60B(loop.crossings[k].bezier) });
}
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({
bezier: takeRot120B(loop.crossings[k].bezier)
});
}
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({
bezier: takeRot180B(loop.crossings[k].bezier)
});
}
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({
bezier: takeRot240B(loop.crossings[k].bezier)
});
}
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({
bezier: takeRot300B(loop.crossings[k].bezier)
});
}
} else {
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({
bezier: takeRot300B(loop.crossings[k].bezier)
});
}
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({
bezier: takeRot240B(loop.crossings[k].bezier)
});
}
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({
bezier: takeRot180B(loop.crossings[k].bezier)
});
}
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({
bezier: takeRot120B(loop.crossings[k].bezier)
});
}
for (let k = 0; k < ncr; ++k) {
loop.crossings.push({ bezier: takeRot60B(loop.crossings[k].bezier) });
}
}
}
return loop;
function prepareOneLoop(hexa, kp) {
let crossing;
const loop = { crossings: [] };
if (hexa.isAlongAxisA && hexa.sideOfPoint[kp] == 4) {
loop.symA = true;
}
while (true) {
let { kout, symm } = hexa.pickFromConnectables(kp);
hexa.connect(kp, kout);
crossing = { hexa, kin: kp, kout, symm };
loop.crossings.push(crossing);
if (symm == "A" || (hexa.isAlongAxisA && hexa.sideOfPoint[kout] == 4)) {
if (loop.symA) return loop; // crossing axis A for the 2nd time : over
if (loop.symB) {
delete loop.symB;
loop.ring = true;
loop.endA = true;
return loop;
}
// crossing axis A on non-symm loop : re-start at the opposite end of this loop
loop.symA = true;
reverseCrossings();
hexa = loop.crossings.at(-1).hexa;
kout = loop.crossings.at(-1).kout;
}
if (symm == "B") {
if (loop.symB) return loop; // crossing axis B for the 2nd time : over
if (loop.symA) {
delete loop.symA;
loop.ring = true;
loop.endB = true;
return loop;
}
// crossing axis B on non-symm loop : re-start at the opposite end of this loop
loop.symB = true;
reverseCrossings();
hexa = loop.crossings.at(-1).hexa;
kout = loop.crossings.at(-1).kout;
}
// take point corresponding to (Hexa, kout) in the adjacent hexagon
({ hexa, kp } = hexa.otherPoint(kout));
if (hexa == loop.crossings[0].hexa && kp == loop.crossings[0].kin) {
return loop; // closed loop without symmetry
}
} // while true;
return loop;
function reverseCrossings() {
loop.crossings.reverse();
loop.crossings.forEach((cr) => ([cr.kin, cr.kout] = [cr.kout, cr.kin]));
}
} // prepareOneLoop
} // makeOneLoop
} // makeLoops
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function toBezier(crossing) {
/* computes the 4 points for a Bezier cubic curve
*/
const ztd = 0.6; // coefficient for straight lines
const zdt = 0.2; // coefficient for U-turn
let pa, pb; // control points of the Bézier curve
let dx, dy, dd;
let kCommVert; // index of common vertex
let din, dout;
let {
hexagon: hexa,
pin: p0,
ksidein: kside0,
pout: p1,
ksideout: kside1
} = crossing;
// the curve is drawn as if entering the hexagon through point p0 and leaving it through point p1
let bin = kside0;
let bout = kside1;
let tp = perpendicular; // table of perpendiculars
/* bout - bin gives (in 1/6 of turn) the direction change of the curve between entry and exit
*/
switch (bout - bin) {
case 3: // straightforward
case -3:
dd = ztd * rayHex; // probably not the smartest way
pa = [p0[0] + tp[bin][0] * dd, p0[1] + tp[bin][1] * dd];
pb = [p1[0] + tp[bout][0] * dd, p1[1] + tp[bout][1] * dd];
break;
case 1:
case -1:
case 5:
case -5:
/* 120 degrees : curve around a vertex
compute distances from p0 and p1 to that vertex and use these distances
to compute position of intermediate Bezier control points pa and pb
*/
if (bout - bin == -1 || bout - bin == 5) {
kCommVert = bin;
} else {
kCommVert = bout;
}
din = distance(hexa.vertices[kCommVert], p0);
dout = distance(hexa.vertices[kCommVert], p1);
dd = 0.6;
pa = [p0[0] + tp[bin][0] * dd * dout, p0[1] + tp[bin][1] * dd * dout];
pb = [p1[0] + tp[bout][0] * dd * din, p1[1] + tp[bout][1] * dd * din];
break;
case 2:
case -2:
case 4: // 60 degrees
case -4:
dd = 0.55 * rayHex; // probably not the smartest way
pa = [p0[0] + tp[bin][0] * dd, p0[1] + tp[bin][1] * dd];
pb = [p1[0] + tp[bout][0] * dd, p1[1] + tp[bout][1] * dd];
break;
case 0: // U-turn
dx = p1[0] - p0[0];
dy = p1[1] - p0[1];
dd = zdt * rayHex;
pa = [p0[0] + tp[bin][0] * dd, p0[1] + tp[bin][1] * dd];
pb = [p1[0] + tp[bin][0] * dd, p1[1] + tp[bin][1] * dd];
break;
default:
throw "unforeseen angle" + bout - bin;
} // switch
return [p0, pa, pb, p1];
} // toBezier;
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
function getPath(loop) {
/* detects extreme points for gradient at the same time */
let pth = new Path2D();
pth.moveTo(loop.crossings[0].bezier[0][0], loop.crossings[0].bezier[0][1]);
loop.crossings.forEach((cr) => {
pth.bezierCurveTo(
cr.bezier[1][0],
cr.bezier[1][1],
cr.bezier[2][0],
cr.bezier[2][1],
cr.bezier[3][0],
cr.bezier[3][1]
);
});
pth.closePath();
loop.path = pth;
return pth;
} // getPath
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function makeHierarchy() {
hierar = { hier: -1, children: [] };
tbLoops.forEach((loop) => insert(hierar, loop));
function insert(hierar, loop) {
/* if point of loop is in any of hierar's children, insert it in this child
else if a point of children is in loop, put it in loop's children (and remove it from this level)
else add loop to this level's children
*/
let pLoop = loop.crossings[0].bezier[0]; // 1st point of bezier
let sch = hierar.children.findIndex((child) =>
child.hier.copies.some((cop) =>
ctx.isPointInPath(cop, pLoop[0], pLoop[1])
)
);
if (sch != -1) insert(hierar.children[sch], loop);
else {
let nhier = { hier: loop, children: [] };
for (let sch = hierar.children.length - 1; sch >= 0; --sch) {
let child = hierar.children[sch];
let p = child.hier.crossings[0].bezier[0];
if (loop.copies.find((cop) => ctx.isPointInPath(cop, p[0], p[1]))) {
nhier.children.push(hierar.children.splice(sch, 1)[0]);
}
}
hierar.children.push(nhier);
}
}
} // make hierarchy
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function drawThisLevel(hierar, ctx) {
ctx.resetTransform();
ctx.translate(maxx / 2, maxy / 2);
ctx.rotate(mPI / 2);
ctx.fillStyle = hierar.rgr;
ctx.strokeStyle = "#000";
ctx.lineWidth = 0.75;
if (hierar.hier === -1) {
ctx.fillRect(-maxy / 2, -maxx / 2, maxy, maxx);
} else {
hierar.hier.copies.forEach((cop) => {
ctx.fill(cop);
if (uiv.stroke) ctx.stroke(cop);
});
}
ctx.resetTransform();
} // drawThisLevel
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function drawHierar(hierar, ctx) {
drawThisLevel(hierar, ctx);
hierar.children.forEach((hier) => drawHierar(hier, ctx));
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function drawOneLevel(level, ctx) {
// level == 0 for background, higher values for inner levels
let nothing = true;
tryThis(hierar, ctx, 0);
return nothing; // will return true when tried beyond deepest level
function tryThis(hierar, ctx, triedLevel) {
if (triedLevel == level) {
drawThisLevel(hierar, ctx);
nothing = false;
} else
hierar.children.forEach((hier) => tryThis(hier, ctx, triedLevel + 1));
}
} // drawOneLevel
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function colorizeLoops() {
/* and calculates hierarchical depth level - 0 for background */
const invGrad = intAlea(2);
const globHue = intAlea(360);
const globSat = intAlea(50, 100);
const biHue = (globHue + intAlea(180 - 100, 180 + 100)) % 360;
const biSat = intAlea(50, 100);
tbLoops.forEach((loop) => {
// find innemost / outermost point of curve
loop.ef = new ExtremeRadialFilter();
loop.crossings.forEach((cr) =>
loop.ef.filterBezier(
cr.bezier[0],
cr.bezier[1],
cr.bezier[2],
cr.bezier[3]
)
);
});
let rings = [];
(function findRings(hierarchy) {
if (hierarchy.hier !== -1 && hierarchy.hier.ring) rings.push(hierarchy);
if (hierarchy.children) hierarchy.children.forEach((h) => findRings(h));
})(hierar);
(function colourLoops(hierarchy, hue, invert, level) {
hierarchy.level = level;
/* "invert" is 0 or 1, and is relative to "normal"(0) or "inverted"(1) gradient */
switch (uiv.colormode) {
case 3:
hue = [globHue, biHue][level & 1];
break;
case 4:
hue = globHue;
}
hierarchy.hue = hue;
if (hierarchy.hier === -1 || hierarchy.hier.ring) invert = 0;
hierarchy.sat = [
intAlea(50, 100),
100,
[globSat, biSat][level & 1],
globSat,
0
][uiv.colormode - 1];
let tblum, lum0, lum1;
switch (uiv.colormode) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
tblum = [40, 80];
break;
case 4:
tblum = [30, 85];
break;
case 5:
tblum = [20, 90];
}
lum0 = tblum[invert ^ invGrad];
lum1 = tblum.reverse()[invert ^ invGrad];
hierarchy.lum0 = lum0;
hierarchy.lum1 = lum1;
if (hierarchy.hier == -1) {
const rMax = (nbLayers + 0.5) * rayHex * rac3;
const rMin = rings[0] ? rings[0].hier.ef.rmin : 0;
hierar.rgr = ctx.createRadialGradient(0, 0, rMin, 0, 0, rMax);
} else if (hierarchy.hier.ring) {
let k = rings.indexOf(hierarchy);
const rMax = hierarchy.hier.ef.rmax;
const rMin = rings[k + 1] ? rings[k + 1].hier.ef.rmin : 0;
hierarchy.rgr = ctx.createRadialGradient(0, 0, rMin, 0, 0, rMax);
} else {
hierarchy.rgr = hierarchy.hier.ef.getRadialGradient();
}
hierarchy.rgr.addColorStop(0, `hsl(${hue} ${hierarchy.sat}% ${lum0}%)`);
hierarchy.rgr.addColorStop(0.5, `hsl(${hue} ${hierarchy.sat}% 50%)`);
hierarchy.rgr.addColorStop(1, `hsl(${hue} ${hierarchy.sat}% ${lum1}%)`);
if (hierarchy.children) {
for (let k = 0; k < hierarchy.children.length; ++k) {
colourLoops(
hierarchy.children[k],
(hue + alea(180 - 100, 180 + 100)) % 360,
1 - invert,
level + 1
);
} // for on children
} // if
})(hierar, globHue, 0, 0);
} // colorizeLoops
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
// - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
let animate;
{
// scope for animate
let animState = 0;
let tInit, currentLevel;
let alpha;
animate = function (tStamp) {
let message;
message = messages.shift();
if (message && message.message == "reset") animState = 0;
if (message && message.message == "click") animState = 0;
window.requestAnimationFrame(animate);
switch (animState) {
case 0:
if (!startOver()) break;
tInit = tStamp;
++animState;
drawOneLevel(0, ctx); // draw background
ctxAnim.canvas.style.opacity = 0;
currentLevel = 1;
drawOneLevel(currentLevel, ctxAnim); // draw animation canvas
case 1:
alpha = mmin(1, (tStamp - tInit) / 2000);
ctxAnim.canvas.style.opacity = alpha;
if (alpha == 1) {
tInit = tStamp;
ctxAnim.clearRect(0, 0, ctxAnim.canvas.width, ctxAnim.canvas.height);
ctxAnim.canvas.style.opacity = 0;
drawOneLevel(currentLevel, ctx);
++currentLevel;
if (drawOneLevel(currentLevel, ctxAnim)) {
tInit = tStamp;
++animState; // drawn all levels
}
}
break;
case 2:
if (tStamp - tInit > 5000) ++animState;
break;
case 3:
tInit = tStamp;
startOver();
drawOneLevel(0, ctxAnim); // draw background
currentLevel = 0;
animState = 1;
} // switch
}; // animate
} // scope for animate
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function startOver() {
if (uiv.random) {
ui.cellsize.value = alea(
parseFloat(ui.cellsize.getAttribute("min")),
parseFloat(ui.cellsize.getAttribute("max"))
);
ui.geometrychoice.value = intAlea(1, 5);
const vmode = intAlea(1, 6);
ui.colormode.value = vmode;
ui.stroke.checked = vmode < 4;
readUI();
}
// canvas dimensions
maxx = window.innerWidth;
maxy = window.innerHeight;
// maxx = 500;
// maxy = 500;
// canv.style.left = ((window.innerWidth) - maxx) / 2 + 'px';
// canv.style.top = ((window.innerHeight) - maxy) / 2 + 'px';
if (canv.width != maxx) canv.width = maxx;
if (canv.height != maxy) canv.height = maxy;
ctxAnim.canvas.width = maxx;
ctxAnim.canvas.height = maxy;
lRef = msqrt(maxx * maxy);
rayHex = uiv.cellsize * lRef;
geometryChoice = uiv.geometrychoice - 1;
/* position of hexagon vertices, relative to its center */
vertices = [[], [], [], [], [], []];
// x coordinates, from left to right
vertices[3][0] = -rayHex;
vertices[2][0] = vertices[4][0] = -rayHex / 2;
vertices[1][0] = vertices[5][0] = +rayHex / 2;
vertices[0][0] = rayHex;
// y coordinates, from top to bottom
vertices[4][1] = vertices[5][1] = -rayHex * rac3s2;
vertices[0][1] = vertices[3][1] = 0;
vertices[1][1] = vertices[2][1] = rayHex * rac3s2;
createGrid();
grid.forEach((hex) => hex.size());
makeLoops();
let mat60 = new DOMMatrix([0.5, -rac3s2, rac3s2, 0.5, 0, 0]);
let mat120 = new DOMMatrix([-0.5, rac3s2, -rac3s2, -0.5, 0, 0]);
let mat180 = new DOMMatrix([-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0]);
let mat240 = new DOMMatrix([-0.5, -rac3s2, rac3s2, -0.5, 0, 0]);
let mat300 = new DOMMatrix([0.5, rac3s2, -rac3s2, 0.5, 0, 0]);
let matSymA = new DOMMatrix([1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0]);
tbLoops.forEach(getPath);
tbLoops.forEach((loop) => (loop.copies = [loop.path]));
// create rotated and symmetric copies of path when required
let nbl = tbLoops.length;
for (let k = 0; k < nbl; ++k) {
let loop = tbLoops[k];
if (loop.ring) continue;
let pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(loop.path, mat60);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(loop.path, mat120);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(loop.path, mat180);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(loop.path, mat240);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(loop.path, mat300);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
if (!loop.symA && !loop.symB) {
let pth2 = new Path2D();
pth2.addPath(loop.path, matSymA);
loop.copies.push(pth2);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(pth2, mat60);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(pth2, mat120);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(pth2, mat180);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(pth2, mat240);
loop.copies.push(pth);
pth = new Path2D();
pth.addPath(pth2, mat300);
loop.copies.push(pth);
}
}
makeHierarchy();
colorizeLoops();
return true;
} // startOver
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
function clickCanvas() {
if (event.target.tagName == "CANVAS") messages.push({ message: "click" });
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
// beginning of execution
{
canv = document.createElement("canvas");
canv.style.position = "absolute";
document.body.appendChild(canv);
ctxAnim = canv.getContext("2d");
canv.style.zIndex = 9;
canv.addEventListener("click", clickCanvas);
} // canvas for grid
{
canv = document.createElement("canvas");
canv.style.position = "absolute";
document.body.appendChild(canv);
ctx = canv.getContext("2d");
} // canvas creation
perpendicular = [];
// perpendicular entering the hexagon
perpendicular[0] = [-msqrt(3) / 2, -1 / 2]; // perpendicular to side 0
perpendicular[1] = [0, -1]; // perpendicular to side 1
perpendicular[2] = [msqrt(3) / 2, -1 / 2]; // perpendicular to side 2
perpendicular[3] = [msqrt(3) / 2, 1 / 2]; // perpendicular to side 3
perpendicular[4] = [0, 1]; // perpendicular to side 4
perpendicular[5] = [-msqrt(3) / 2, 1 / 2]; // perpendicular to side 5
canv.addEventListener("click", clickCanvas);
prepareUI();
messages = [{ message: "reset" }];
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
</script>Conclusion:
And there you have it! With this interactive shape generator, you can effortlessly switch between various shapes and watch them come to life on your canvas. It’s a fantastic way to experiment with canvas animations and add a touch of interactivity to your web projects. If you enjoyed this project and want to explore more creative HTML and CSS designs, be sure to check out FrontBackGeek for a treasure trove of design inspiration and tutorials. Happy coding!
Credit : https://codepen.io/Dillo/details/QWXBXBQ


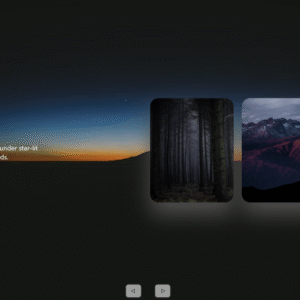




background image slider is not working please help me
what’s the issue?